 Savannah
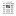
Savannah
The savannah ecosystem is the second most important terrestrial habitat in Ghana after the high forest. This comprises the Guinea Savannah and Sudan Savannah.
| Release date | 14/08/2010 |
|---|---|
| Contributor | Kwesi Anderson |
Ghana falls within two of the savannah ecosystems in West Africa. These are the Guinea Savannah and Sudan Savannah. The savannah ecosystem is the next most important terrestrial habitat in Ghana after the high forest. It accounts for nearly half of the total land area of the country. Rainfall is uni-modal and it is the main determining environmental element, with relatively short duration and decreases northwards. (insert a link to vegetation map of Ghana).
The characteristic feature of the savannah ecosystem is the dominance of relatively short trees with grass, shrub and scrub undergrowth. This floristic characteristic is maintained by the decreased average annual rainfall and recurrent annual bush fires. The density and extent of grass, herbs and scrub undergrowth in most cases depends on the level and extent of disturbances.
The Guinea Savannah ecosystem in Ghana starts from the northern limit of the forest zone emerging out of the dry semideciduous forest (fire zone subtype). The less disturbed area of the Guinea Savannah ecosystem is dominated by relatively short trees with shrub and scrub undergrowth. The Sudan Savannah ecosystem is located to the north of the Guinea Savanna. The vegetation is mainly isolated short trees, scrub and short grass undergrowth.
